Blog
How to Choose the Best Home Solar System for Your Needs?
When selecting a home solar system, the choice can feel overwhelming. According to Dr. Emily Hart, a leading expert in renewable energy, "Every home is unique, and so are its energy needs." Understanding these needs is crucial in making the right decision.
The market is flooded with various options. Brands, prices, and technologies can confuse even the savviest consumer. It is essential to know your energy usage patterns and the available space for solar panels. As you dive into the selection process, consider what features matter most to you.
Many overlook the importance of local regulations and incentives. They can significantly impact your final decision. A small misstep here could lead to dissatisfaction later. Be aware of your choices and their long-term effects on your home and budget. It’s vital to ask questions and reflect on what a home solar system truly means for your lifestyle.

Understanding Your Energy Needs and Consumption Patterns
Understanding your energy needs and consumption patterns is crucial when choosing a solar system for your home. Start by analyzing your monthly electricity bill. Look for patterns in usage throughout the year. Note peak usage months, particularly during summer or winter. This analysis helps gauge how much energy you truly need.
Consider how many devices you use daily. Appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, and electronics consume varying amounts of energy. Understanding this can aid in sizing your solar system correctly. You might think you need a larger system, only to find out that some months have lower usage.
Take a moment to reflect on your habits. Do you leave lights on? How often does the family watch TV? These choices impact your consumption. Tracking usage patterns can unveil ways to save energy. Even small changes will reflect in your solar energy needs. It's essential to align your solar system with your lifestyle for optimal efficiency.
How to Choose the Best Home Solar System for Your Needs?
| Category | Details | Estimated Annual Consumption (kWh) | Recommended Solar System Size (kW) | Average Cost ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Household | 1-2 people, minimal appliances | 3,000 | 3-4 | 3,500 |
| Medium Household | 3-4 people, standard appliances | 7,000 | 5-6 | 7,500 |
| Large Household | 5+ people, multiple devices | 10,000 | 7-8 | 10,000 |
| Energy-Efficient Household | Focused on energy savings | 5,000 | 4-5 | 6,000 |
Choosing the Right Type of Solar Panels for Your Home
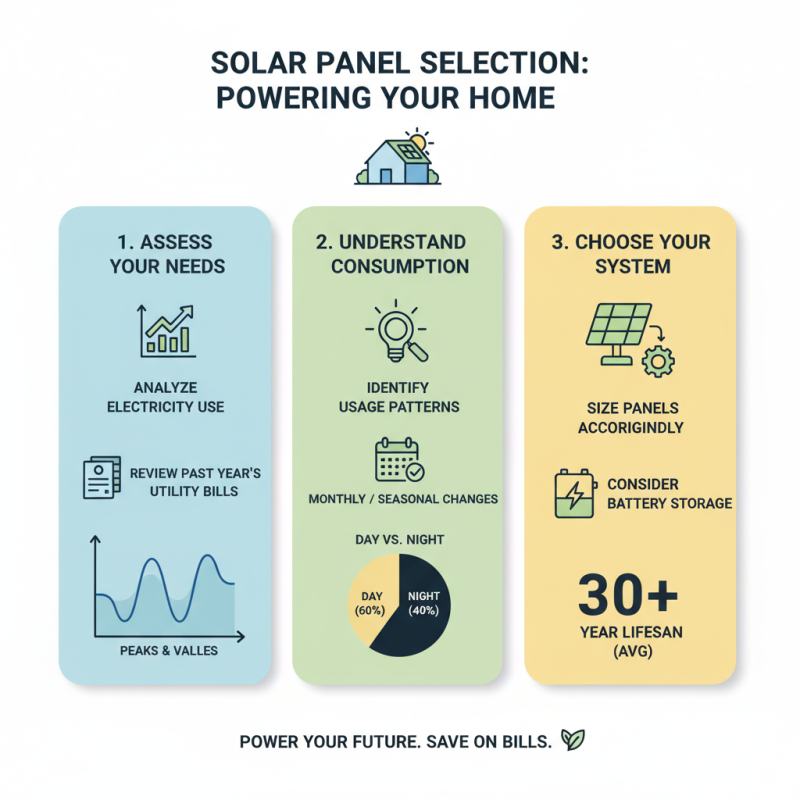
When choosing solar panels for your home, consider your energy needs carefully. Start by analyzing your electricity consumption. Look at your utility bills from the past year. This gives a clear picture of how much energy you typically use. It’s often surprising to see the peaks and valleys in energy usage.
Next, explore the types of solar panels available. Monocrystalline panels are known for high efficiency. They might be a good fit if space is limited. Polycrystalline panels are often more affordable but may take up more space. Thin-film panels are lightweight and flexible. However, they usually have lower efficiency rates. Each type has its pros and cons, which may require some thoughtful consideration.
Installation is another crucial point. Make sure you have a solid roof to support the panels. Aging roofs should be assessed before installation. Additionally, consider local climate conditions. Some panels perform better in certain weather. Review your options thoroughly. It’s okay to ask for professional recommendations, but don’t forget to do your own research. The decision can feel daunting at times, but informed choices lead to better outcomes.
Evaluating Solar Inverters and Their Impact on Efficiency
When selecting a home solar system, one key component is the solar inverter. This device converts direct current (DC) from solar panels into alternating current (AC) for home use. The efficiency of the inverter directly impacts overall energy generation. If the inverter is not efficient, you could lose a significant amount of power.
Consider the different types of inverters available. Some are string inverters, which connect multiple panels together. Others are microinverters, which operate independently for each panel. Each option has strengths and weaknesses. A string inverter might be simpler and lower-cost, but it can suffer from shading issues. Microinverters can maximize energy production but come at a higher upfront price. Balancing cost versus performance is crucial.
Look into the inverter's efficiency rating, as well. An inverter with a high rating will convert more solar energy into usable electricity. However, high-efficiency models can be pricey. It’s tempting to aim for the best-rated model, but weigh that against your budget and energy needs. Reflect on how much energy you actually consume. This understanding will help you choose wisely and avoid overspending on features you might not need.
Comparing Solar Battery Options for Energy Storage Solutions
When considering solar battery options, think about your energy needs. Different batteries offer varied capacities. It’s important to select one that meets your daily requirements. Lithium-ion batteries are popular for their longevity and efficiency. However, options like lead-acid batteries are cheaper and might suit smaller homes. Assess how much energy you consume each day. This will aid in choosing the right storage.
Tip: Always check battery cycle life and warranty. A longer cycle life means better long-term value. Make sure the battery can handle peak loads. It should also integrate well with your solar system for maximum efficiency.
Not all batteries are created equal. Some may not perform optimally under specific conditions. It’s essential to consider local climate effects. For example, extremely hot or cold weather can impact battery performance. Researching user experiences can uncover potential drawbacks. Seek feedback from homeowners in your area.
Comparison of Solar Battery Options for Home Energy Storage
Assessing Installation Costs and Available Incentives or Rebates
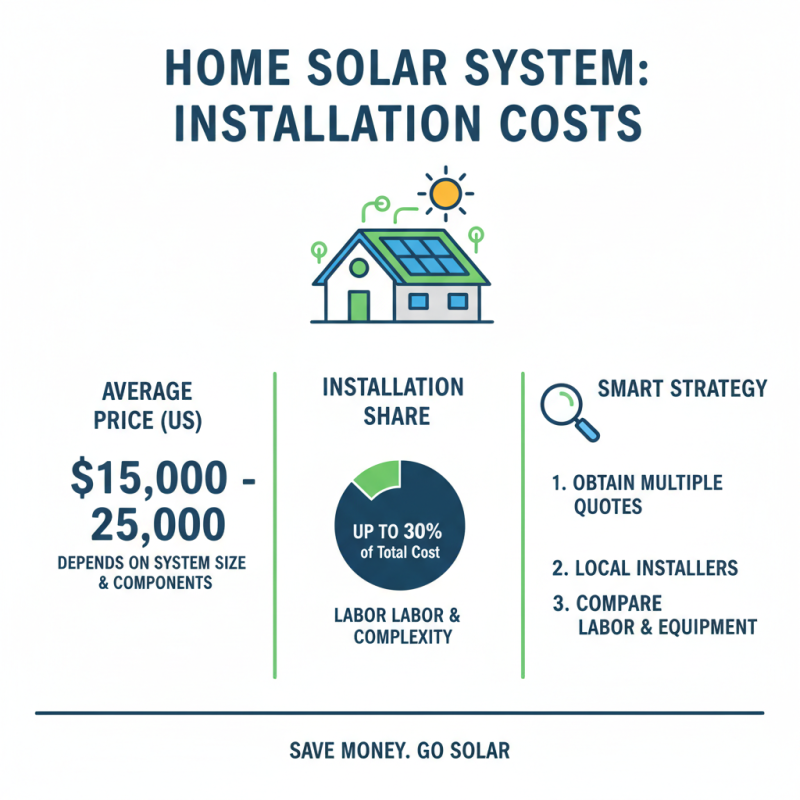
When assessing the installation costs of a home solar system, homeowners must consider several factors. The average price for a residential solar array in the U.S. ranges from $15,000 to $25,000, depending on the system size and components used. Installation can account for up to 30% of this cost. It's vital to obtain multiple quotes from local installers. Each quote may vary based on labor costs and installation complexity.
Available incentives and rebates significantly impact the overall expense. The Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) allows homeowners to deduct 26% of the system’s cost from their federal taxes. Many states also offer additional benefits. For example, California provides a rebate program that can further reduce costs. However, not every homeowner qualifies for all incentives, leading to potential confusion.
It's crucial to research the specifics of local incentive programs. Many residents overlook the need for a professional audit before installation. This step may uncover additional savings or potential obstacles. Every home presents unique energy needs that affect the overall investment in solar technology. Understanding these nuances is key to making an informed decision.
Related Posts
-

How to Maximize Solar Power Efficiency: Proven Strategies and Data Insights
-

Top Benefits of Solar Installation for Homeowners in 2023
-

2025 Top Solar Panel System Trends and Benefits You Need to Know
-

Transform Your Energy Bills: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing Solar Panels for Your Home
-

Exploring Solar Energy Innovation Trends at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

How to Choose the Best Solar Panels for Your Home in 2023
