Blog
2025 Guide: How to Choose the Best Residential Solar Systems for Your Home
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources, residential solar systems have become a viable and popular option for homeowners seeking to reduce their carbon footprint and utility costs. By harnessing the sun's energy, these systems provide a sustainable way to power homes while contributing to global efforts to combat climate change. However, with numerous options available on the market, selecting the right residential solar system can be a daunting task for many.
In this guide, we will explore key considerations that homeowners should keep in mind when choosing the most suitable residential solar system for their needs. Factors such as energy requirements, geographic location, system types, and available incentives will be examined to help you make an informed decision. Whether you are looking to make a significant investment or simply curious about solar energy, understanding these elements is essential to optimizing your home’s solar potential and maximizing the benefits of your investment.

Understanding the Basics of Residential Solar Systems
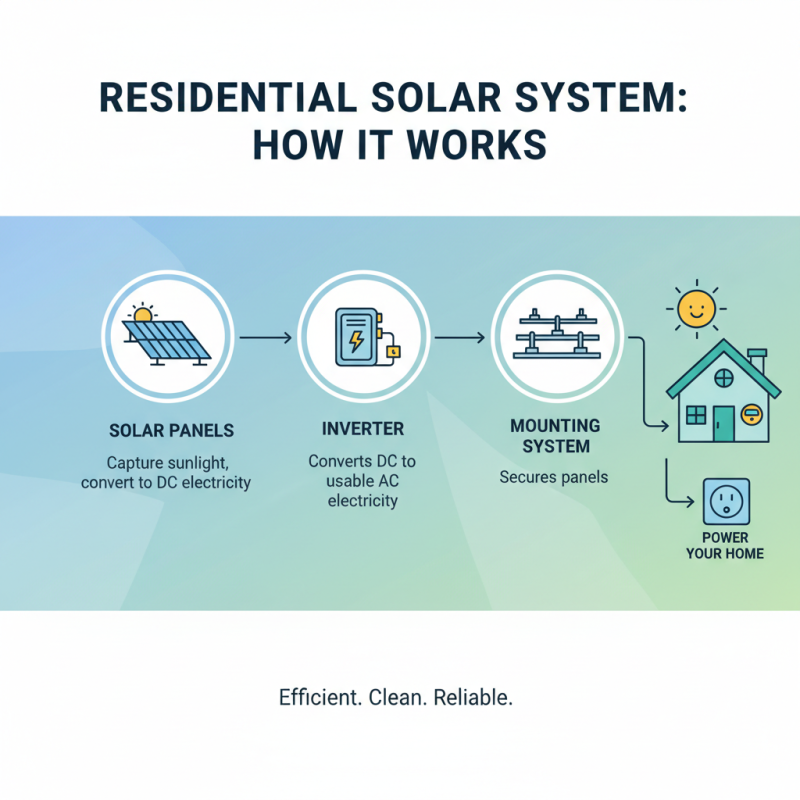
When considering the installation of a residential solar system, it’s essential to understand the fundamental components and how they function together. A typical solar system comprises solar panels, an inverter, and a mounting system. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, while the inverter transforms this direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which can be used in your home. The mounting system secures the panels in place, ensuring they can efficiently capture sunlight.
**Tips:** When selecting solar panels, consider their efficiency ratings and warranty options. Higher efficiency panels may initially cost more but can save more on energy bills over time.
Understanding your household’s energy needs is also crucial. By analyzing your energy consumption, you can determine the size of the solar system that will best meet your requirements. This analysis helps in deciding between different system sizes and types, enabling you to choose one that fits your lifestyle and budget.
**Tips:** Monitor your energy usage in different seasons, as it fluctuates with heating and cooling needs. This data can guide you in selecting a solar system that covers your peak energy consumption periods effectively.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Solar Panels
When choosing solar panels for your home, several key factors should be taken into account to ensure you select the best residential solar system that meets your energy needs. First, consider the efficiency of the solar panels. Higher efficiency panels convert more sunlight into electricity, allowing you to generate more power in limited space. This is especially important if you have a smaller roof or face shading issues.
Another critical factor is the durability and weather resistance of the panels. Look for panels that are tested for harsh conditions, such as extreme heat, heavy rain, and hail. Solar systems are a long-term investment, and choosing durable options will minimize maintenance and replacement costs over time.
**Tips:** Ensure you check the warranty of the solar panels as well. A longer warranty indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in the product’s longevity. Additionally, research installation companies carefully; a professional and experienced installer can significantly impact the efficiency and performance of your solar system. Always request multiple quotes to ensure you are getting a fair price and service.
2025 Guide: Solar Panel Efficiency Comparison
This chart compares the efficiency of different types of solar panels available in 2025, helping homeowners make informed decisions when choosing the best residential solar systems for their needs.
Evaluating Inverters and Their Impact on Energy Efficiency
When selecting a residential solar system, understanding the role of inverters is crucial for maximizing energy efficiency. Inverters are essential components that convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is usable for household appliances. The type and quality of inverter you choose can significantly impact the overall performance of your solar energy system. High-quality inverters offer better energy conversion rates, ensuring you make the most of the sunlight your panels capture.
There are several types of inverters available, including string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers. String inverters are typically used in systems with uniform solar panel exposure, while microinverters can optimize energy production for individual panels, making them a suitable choice for roofs with shaded areas. Power optimizers work alongside string inverters to enhance energy output by adjusting the performance of each panel. Evaluating these options based on your home's specific needs and design can lead to improved energy efficiency and lower electricity costs, ultimately optimizing your solar investment.
2025 Guide: How to Choose the Best Residential Solar Systems for Your Home - Evaluating Inverters and Their Impact on Energy Efficiency
| Inverter Type | Efficiency Rating (%) | Cost ($) | Warranty (Years) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| String Inverter | 95 | 1500 | 5 | Cost-effective, Simplified Installation |
| Microinverter | 96 | 2200 | 25 | Improved Performance, Module-Level Monitoring |
| Power Optimizer | 97 | 1800 | 20 | Enhanced Energy Harvesting, Flexible System Design |
| Hybrid Inverter | 98 | 3000 | 10 | Battery Storage Integration, Versatile Usage |
Assessing Installation Options: DIY vs. Professional Services
When considering the installation of residential solar systems, homeowners face a crucial decision: whether to tackle the installation themselves or to enlist the services of professional installers. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges, impacting both costs and system performance. A report by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) indicates that professionally installed solar systems typically result in better overall savings, as expert installers ensure optimal placement and connections, which can enhance energy production by up to 20% compared to DIY installations.
DIY installation may initially appear more cost-effective, with estimates suggesting potential savings ranging from 30% to 50% on labor costs alone. However, as indicated by a survey conducted by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), nearly 60% of DIY projects experience setbacks due to inexperience, leading to increased long-term costs. These issues often stem from improper installation techniques, which can ultimately compromise system efficiency and even lead to safety hazards. Homeowners must weigh these factors against their own skills and the time commitment required for a successful installation.
In summary, while DIY solar installation offers potential initial savings, the benefits of hiring professional services often outweigh the risks associated with installation errors. Industry data supports the notion that a professionally installed system not only increases energy production but also provides peace of mind, assuring homeowners of reliability and performance. As such, it is vital for homeowners to carefully evaluate their options, assessing both their capabilities and the long-term implications of their choice.
Exploring Financing and Incentives for Solar System Installation
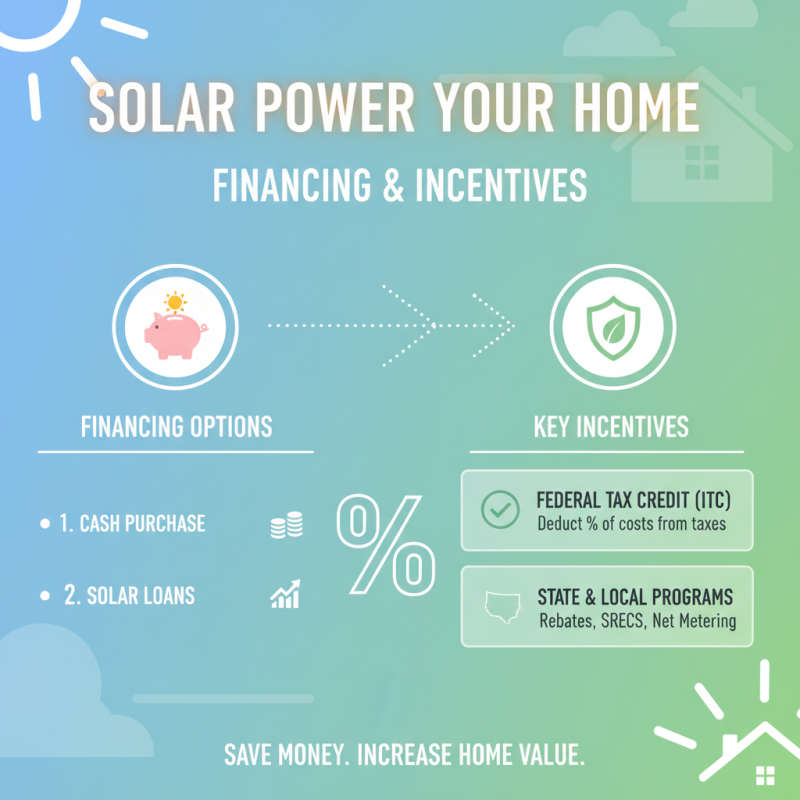
When considering the installation of a residential solar system, understanding the different financing options and incentives available can significantly impact your decision. Several programs offered at the federal and state levels can help offset the initial costs, making solar energy more accessible for homeowners. Federal tax credits, such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), allow homeowners to deduct a considerable percentage of their solar installation costs from their federal taxes. This incentive not only encourages investment in renewable energy but also helps homeowners recoup a portion of their expenditures quickly.
Alongside tax credits, many states provide additional incentives, such as rebates, grants, and performance-based incentives, which can further lower the cost of solar systems. For example, some states may offer upfront rebates that provide a cash incentive for installing solar panels, while others might have net metering policies that allow homeowners to receive credits on their utility bills for the excess electricity generated by their solar systems. Moreover, financing options like solar loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs) make it easier for homeowners to adopt solar energy without upfront costs, allowing them to pay for their systems over time while still benefiting from energy savings. Understanding these financing choices and incentives can help homeowners make an informed decision that is financially beneficial in the long run.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top Home Solar Trends You Need to Know for Sustainable Energy Solutions
-

7 Best Benefits of Solar Installation for Your Home in 2023
-

Top Strategies for Successful Solar Installation Projects
-

5 Amazing Benefits of Home Solar System You Need to Know
-
How to Choose the Best Solar Panels for Your Home: A Complete Guide
-

How to Choose the Best Solar Panels for Your Home Needs and Budget
